- Published on
10 Ways to Optimize Your Website Performance
- Authors

- Name
- perfHack
- @perfhackhq
10 Ways to Optimize Your Website Performance
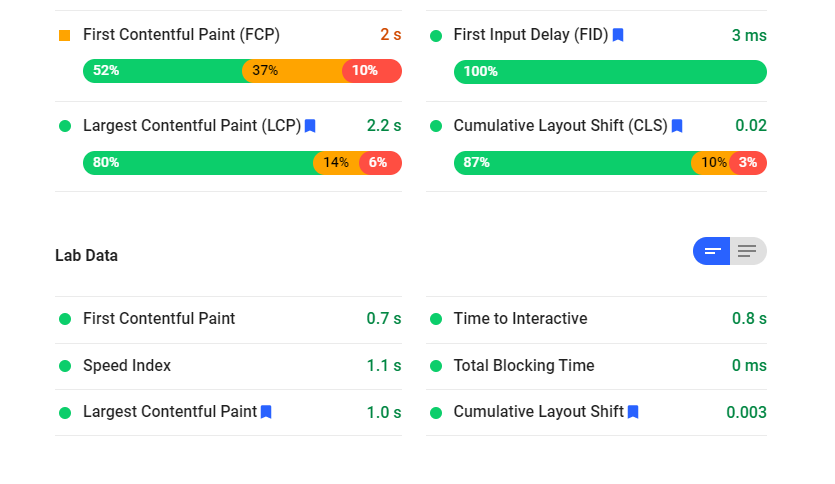
In the digital age, a website's performance is critical to its success. Users expect fast and responsive web experiences, and search engines prioritize well-optimized sites. Here are ten effective ways to ensure your website runs smoothly and retains visitors.
1. Optimize Image Files
Images are often the heaviest elements on a website. Optimizing them for the web can significantly reduce load times. Use formats like JPEG for photographs and PNG for graphics with fewer colors. Tools like Adobe Photoshop or free online services can help compress images without losing quality.
2. Minify and Combine Files
Every piece of JavaScript and CSS adds to the time it takes for your website to load. Minifying these files by removing unnecessary characters and whitespace can reduce their size. Furthermore, combining multiple scripts into a single file reduces the number of HTTP requests needed to load the page.
3. Leverage Browser Caching
Browsers can cache a lot of information, so when a visitor comes back to your site, it doesn't need to reload the entire page. Use this to your advantage by setting appropriate cache-control headers for your website's assets.
4. Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
CDNs distribute your content across multiple, geographically diverse servers, reducing the distance between users and website resources. This means faster loading times as users can download content from a server closest to them.
5. Optimize Code Execution
Optimizing the way your code executes can have a significant impact on performance. For instance, using asynchronous loading for JavaScript allows other elements to load without being blocked by the JS loading process.
6. Enable gzip Compression
gzip is a form of data compression that works well with web content. When enabled, it can reduce the size of your HTML, stylesheets, and JavaScript files. This is a server setting that can be turned on with just a few configuration changes.
7. Minimize Redirects
Each redirect creates additional HTTP requests, which delay page rendering. Minimize them by ensuring that links to internal and external content are direct. If redirects are necessary, make sure they're server-side (like 301 redirects) rather than client-side.
8. Optimize Third-Party Scripts and Plug-ins
Third-party scripts for tracking, advertising, and social media can slow down your site. Evaluate the necessity of each and remove any that are not essential. For those that are, ensure they are loaded asynchronously to prevent them from blocking the page rendering.
9. Monitor Performance
Regular monitoring can help you spot performance issues before they become problematic. Use tools like Google's PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or WebPageTest to analyze your site's performance and follow their optimization recommendations.
10. Implement Lazy Loading
Lazy loading is a design pattern that delays the loading of non-critical resources at page load time. Instead, items like images or videos are loaded only when they're needed — as the user scrolls down the page. This can significantly improve performance, especially on pages with a lot of content.
By implementing these strategies, you can improve your website's performance, enhance user experience, and potentially boost your search engine rankings. Remember, website optimization is an ongoing process, so regular reviews and adjustments are necessary to maintain optimal performance.